
Overview
Cardiomyopathy is a heart condition that affects the heart muscle. In cardiomyopathy, the heart can’t efficiently pump blood to the rest of the body. It affects people of all age groups and races. Cardiomyopathy enlarges the heart muscles, stiffens and thickens the heart muscles, as a result, the pumping ability of the heart is reduced and the heartbeat becomes irregular on the other hand the blood backs up in the lungs and causes congestive heart failure.
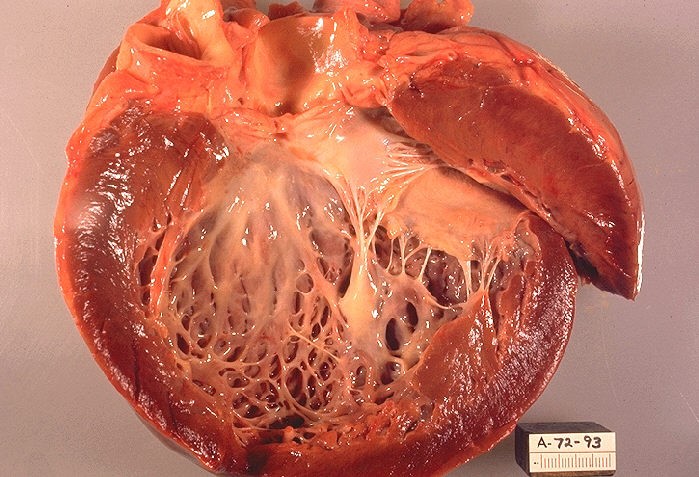
Types of Cardiomyopathy
Three types of cardiomyopathy are common:
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: this is the most common type of cardiomyopathy. In dilated cardiomyopathy, the heart muscles are enlarged and can’t contract during systole so it’s systolic dysfunction. It is also known as “congestive cardiomyopathy”. The enlarged muscles are weak to pump blood and it causes heart failure in the end. It can be inherited but is most commonly caused by coronary artery disease.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: it is a group of inherited conditions that produce hypertrophy of the myocardium. In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the heart muscles get thickened and non-compliant, so the heart can’t relax properly during diastole so-called diastolic dysfunction. It can be caused by long-term hypertension, diabetes and ageing. In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, there is asymmetrical septal hypertrophy that causes left ventricular outflow obstruction.
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: the least common type in which heart muscles get stiffed and scarred due to amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, or hemochromatosis. In this type heart neither contract nor relax.
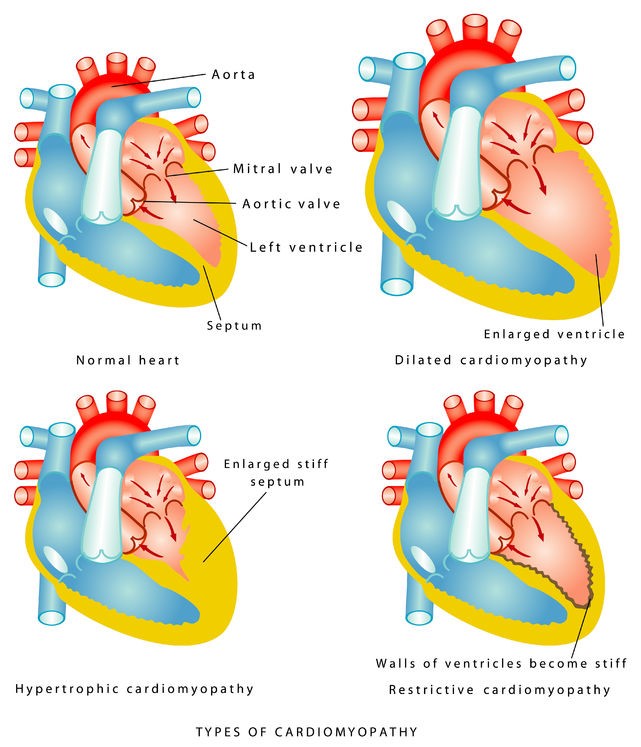
Causes
Cardiomyopathy is either inherited or acquired. Inherited means you are born with cardiomyopathy due to genes that you have from your parents and acquired means cardiomyopathy is developed due to an underlying disease and that may be;
- Connective tissue disorders
- Autoimmune diseases like scleroderma, and polymyositis.
- Infiltrative diseases
- Storage diseases
- Coronary heart diseases or heart attack
- Endocrine diseases
- Mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy like a beta-myosin heavy chain, myosin-binding protein
- Long-term use of alcohol
- Pregnancy
- Infections in the heart
Risk Factors
Cardiomyopathy affect all age groups of people and the major risk factors are given below:
- Family history of cardiomyopathy, heart failure or sudden cardiac death
- Obesity
- Chronic hypertension
- Heart infections like infective endocarditis
- Covid-19 infection
- Diabetes
- Valvular heart diseases
- Thyroid diseases
- Alcohol use
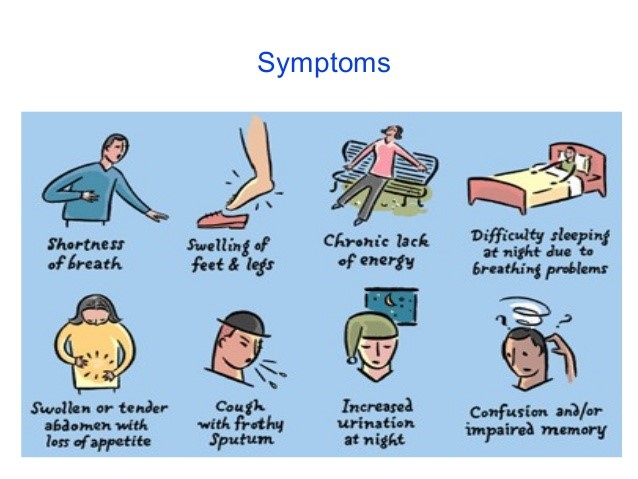
Signs and Symptoms
Almost symptoms of all cardiomyopathy are similar and signs are little bit different.
Symptoms are:
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath) particularly during exertion
- Dizziness, syncope
- Oedema (swelling of legs, ankle and abdomen)
- All symptoms of left-sided and right-sided heart failure
Signs are different in all three types of cardiomyopathy:
In dilated cardiomyopathy, S3/S4 gallop and jugular venous distension occur.
In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy double apical pulsation, jerky carotid pulse and ejection systolic murmur occur.
In restrictive cardiomyopathy, Friedrich’s sign and Kussmaul’s sign occurs.
Treatments
Cardiomyopathy can’t be reversed but the goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms and prevent further damage and loss of functions. The treatment includes;
- Lifestyle changes: lifestyle changes are, avoiding alcohol and cocaine use, quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, reducing stress, getting regular exercise and enough sleep.
- Medications: medications reduce blood pressure, reduce cholesterol and keep the heart in a regular rhythm the medications are warfarin, beta-blockers, ACEI and ARBs and amiodarone for arrhythmias.
- Surgery: if symptoms are severe and medications are not working the surgery is done in such cases, surgeries would be By-pass, valve replacement, pacemakers, implantable defibrillator, septal myomectomy a less common procedure and in the end, cardiac transplant is done if the above procedures fail.
