What is Heart Failure?
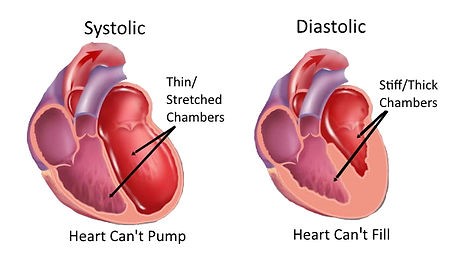
Heart failure is a serious condition but it doesn’t mean the heart stops beating. Heart failure means the heart can’t pump enough blood to the body and other organs to meet its metabolic demands. Heart failure is a chronic and progressive condition and it’s basically the collection of symptoms that stiffen your heart. Heart failure is of 2 types; Systolic dysfunction and Diastolic dysfunction
Systolic dysfunction means impaired contractility. It has a low ejection fraction (the per cent of blood squeezing from the heart which is less than 45%. Normally ejection fraction is 55 to 70%. And Diastolic dysfunction is impaired ventricular filling but the ejection fraction is normal.
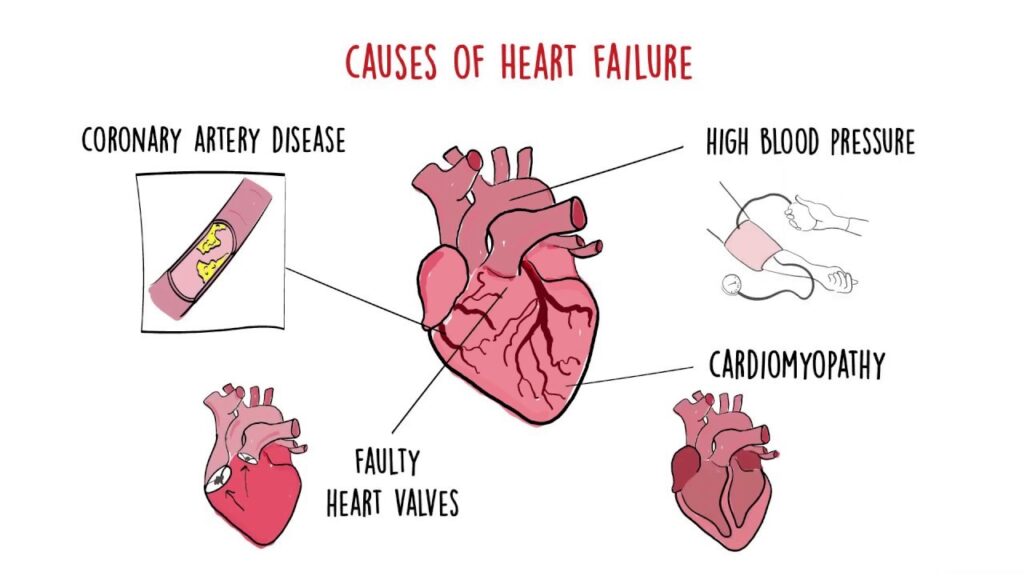
Causes of Heart Failure
Heart failure is mostly due to other conditions. And the most common cause of heart failure is coronary artery disease (CAD), a disorder in which blood supply to the heart is impaired due to narrowing or stiffening of the coronary artery. Other conditions which cause heart failure are
- Hypertension
- Cardiomyopathies
- Congenital heart diseases
- Heart valve diseases
- Heart attack
- Alcohol
- Thyroid diseases
Risk Factors of Heart Failure
Untreated health conditions increase the risk of heart failure. And also unhealthy behaviour and lifestyle increase the risk for heart failure. Some of the health conditions and unhealthy behaviour are listed below:
- Heart attack
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Increase lipid, sodium and sugar intake
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Drug abuse
- Physical inactivity (not getting enough exercise )
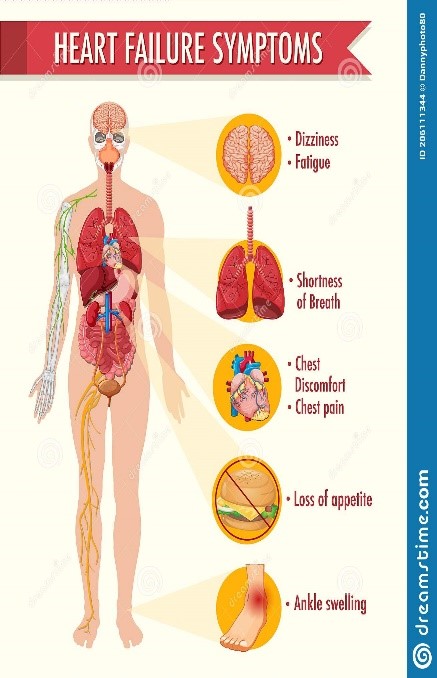
Symptoms of Heart Failure
In left-sided heart failure means the left ventricle is unable to pump enough blood in the aorta so that the body can’t get enough blood and blood back up in the lungs causes;
- shortness of breath
- fatigue
- persistent coughing and
- shortness of breath on lying down.
While in right-sided heart failure the right ventricle can’t push blood to the lungs to collect oxygen. So blood from great veins builds up in veins and causes;
- Lower extremities swelling (leg and ankle oedema)
- Abdominal swelling
- Painful hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Distension of jugular vein
Some general symptoms occur like; weight gain, loss of appetite, fatigue, irregular heart rate and exercise intolerance.
Treatment of Heart failure
Treatment usually involves lifestyle modifications, medications and surgeries if needed. Let’s have look at them one by one;
1: Lifestyle modification
Lifestyle modification is a necessary part of treatment as well as the prevention of heart failure. If you skip this part and only take medication then you can’t get the benefit of medications, and you still suffer. Lifestyle modifications are;
- Cessation of smoking
- Weight reduction
- Low sodium diet (<4g/day)
- Exercise
- Low fat intake
2: Medications
The early stage of heart failure can be treated by medications. Medications relieve the symptoms and cause them to live longer. Medications improve the heart pumping ability, decreases heart rate, decrease the risk of blood clots, reduce cholesterol and remove excess sodium and decrease hypertension.
These medications are;
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (captopril)
- Aldosterone receptor blockers (valsartan)
- Beta-blockers (carvedilol)
- Diuretics (furosemide)
- Nitrates
- Aldosterone antagonist (spironolactone)
- An SGLT2 Inhibitor (dapagliflozin)
3: Surgery
Some people need surgery because there may be a block in arteries which may need procedures to open, may need to replace heart valves or if there is advanced heart failure then cardiac transplant is done.
The procedures are;
Bypass surgery
Percutaneous coronary intervention
Implantable defibrillator
Pacemaker
Cardiac transplantation